C-Glutamine by Iagen Professional
$39.95
$39.95
The Real Deal
I feel a difference. I feel like I workout harder and longer! I also take a few before bedtime to help with recovery. Great supplement, the real deal. I’ve already recommended it to my dad.
100 % Satisfied
My naturopath Dr recommended this form of Glutamine as the most effective and easy to absorb by the body. I’m so happy to have found this one. Taste very pleasantly. I take 2 before my Spinning class and I swear it gives so much more energy and endurance. Will continue to buy!
A Great Help
C-Glutamine has a pleasant taste and mixes well in smoothies and food. After one week of use, my intestine tolerated more foods (less pain and bloat) which in turn created healthier muscle function and endurance. Lived up to its claims and I’d buy again.
Introducing The World’s First Multi-Purpose Super Nutrient
C-Glutamine is a new biologically superior form of the nutrient glutamine. Glutamine is a natural amino acid often used because of the many critical functions and structures it supports. Highly recommended!
What is C-Glutamine?
C-Glutamine is a new type of glutamine supplement which is up to ten times more bioavailable than traditional L-glutamine supplements. C-Glutamine is a delicious, easy-to-take powdered supplement.
What Is Glutamine?
Glutamine is a natural amino acid found in foods and made within the body in small amounts.
Athletes and sports nutritionists have known about glutamine for years because of the support it provides to muscle tissue. Many healthcare professionals also recommend glutamine for intestinal and immune function.
In fact, glutamine supports a surprisingly wide range of critical functions and structures in the body. For this reason, many people are now including glutamine in their daily regimen of supplements because of the many ways it supports health.
What Does Glutamine Do In The Body?
- Fuels immune, heart and intestinal cells*
- Promotes healthy intestinal function*
- Preserves and maintains muscle tissue*
- Promotes growth hormone release*
- Regulates and balance pH*
- Promotes liver detoxification*
- Scavenges toxic ammonia*
It’s A True Multi-Purpose Super Nutrient Everyone Can Use, Every Day.
The Problem With L-Glutamine Supplements
What The Label’s Not Telling You Virtually all other glutamine supplements are L-glutamine. Unfortunately, this type of free-form glutamine is highly unstable and quickly breaks down in the presence of heat, moisture and pH extremes. Our stomachs provide all three of these anti-glutamine conditions. For this reason, some of the glutamine in these supplements is broken down in the stomach before it has a chance to be absorbed by the intestines.
Iagen Professional has solved the problem by creating a unique peptide-bonded glutamine that is far more stable than L-glutamine. The glutamine in C-Glutamine is resistant to stomach pH, moisture and other factors which degrade free form glutamine.
C-Glutamine For Special Circumstances
Certain situations acutely increase the body’s demand for glutamine, making it even more important during times of:
- Recovery from surgery or injury, especially burns*
- Intense physical training or overtraining*
- Inflammatory states*
- Immune system challenges*
C-Glutamine is a very safe supplement. However, if you are pregnant, breastfeeding or being treated for a medical condition consult your doctor before using glutamine or any other dietary supplement.
Suggested Use: Add one or more scoops of C-glutamine to food or blend with any liquids, hot or cold. Consume 1 to 3 times daily. Suitable for pets.
Additional Information From The Manufacturer
C-Glutamine™ is manufactured by Iagen, the makers of: Cardiokinase® and AHCC®. 300 Gram powder – 30 servings. CONTAINS GLUTEN
What Is It?
(Covalent Glutamine) is a dairy free natural source of Covalent Bonded Glutamine enzymatically derived from red wheat berries. The Glutamine is connected to other amino acids on an oligopeptide chain or more specifically covalently bonded to other amino acids.
Benefits of Glutamine
Glutamine has been shown to assist in improving: immune system function, brain function, blood sugar levels, increasing muscle mass, and healing and maintaining the digestive tract. It decreases intestinal permeability by nutritionally supporting and strengthening the mucosa.
“There is increasing evidence that systemic Glutamine functions as an important biosynthesis precursor in intestinal cells by supporting synthesis of Glutathione”
Present Knowledge in Nutrition 7th Edition. p74. By: International Life Sciences Institute.
Why Use C-Glutamine
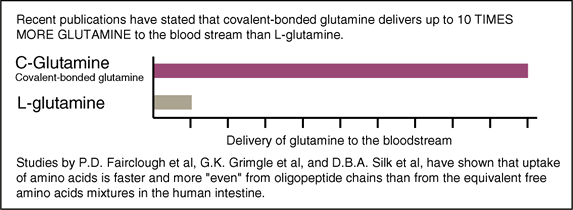
The majority of commercially available Glutamine sources offer only L-Glutamine, a synthetic, free amino acid. L-Glutamine has been shown to be unstable in the presence of heat, water, acid or base solutions, making L-Glutamine impractical to utilize in all but powdered food preparations. Covalent Bonded Glutamine, on the other hand, has been shown to withstand processing temperatures of 180 degrees Fahrenheit for one hour or 250 degrees Fahrenheit for 15 minutes and pH variances in the range of 3.5 to 9.0. In addition, Covalent Bonded Glutamine is stable in aqueous solutions for prolonged periods of time. Covalent Bonded Glutamine can be used in all liquid and semi-solid food preparations. In addition, due to the instability of L-Glutamine in water and pH extremes, it is safe to assume that much of L-Glutamine decomposes once it passes into the human gastrointestinal tract. Gastric acid is equivalent to 0.1 Normal Hydrochloric Acid (pH less than 2) and at 98.6 degrees Fahrenheit and a pH below 2, L-Glutamine decomposes very quickly. In addition, since L-Glutamine is a free amino acid, what percentage that does survive the pH extremes of the stomach is absorbed through the intestinal wall by a different mechanism than covalent bound amino acids…this free amino acid absorption mechanism is competitive… meaning that in an excess of free amino acids, only a certain percentage of any particular free amino acid will be absorbed. Covalent Bonded Glutamine, on the other hand demonstrates improved retention in intestinal cells and the oligopeptides containing Glutamine will be absorbed through the intestinal wall by a less “competitive” method. Studies by P.D. Fairclough et al., G.K. Grimble et al, and D.B.A. Silk et al, have shown that uptake of amino acids is faster and more “even” from oligopeptide chains than from the equivalent free amino acid mixtures in the Human intestine. In other words, Covalent Bonded Glutamine will be absorbed faster and probably more efficiently than L-Glutamine in the Human digestive system. Recent publications have stated that Covalent bonded glutamine delivers up to 10 times more glutamine to the blood stream than L-glutamine.
C-Glutamine is a spray-dried form of glutamine, which is stabilized to withstand changing temperature, pH, and aqueous environments by the glutamine being covalently bonded to other amino acids. The product is a mixture of oligopeptides. Covalent bonded glutamine has been shown to be stable over prolonged periods of time to high temperatures, pH variations, and resists breakdown in aqueous dispersions, unlike free form L-glutamine.
C-Glutamine is available as a powdered supplement. Each scoop contains one gram of covalently bonded glutamine. The recommended dosage of C-Glutamine is five grams (1 scoop) per day in divided doses. C-Glutamine may be mixed with liquids or sprinkled on food, and is suitable for pets.
Iagen Professional – http://www.iagen.com
Related Videos
Autoimmune Dr. Chad Larson Gluten Free Immune System Keep It Real Leaky Gut
Keep It Real Episode 12: Arthritis, Autoimmunity & Leaky Gut
Watch VideoDr. Chad Larson Keep It Real Leaky Gut Microbiome
What Is Leaky Gut & How You Can Fix It
Watch VideoDr. Chad Larson Food Gluten Free Inflammation
Food Allergy, Intolerance, & Sensitivity: What’s the Difference?
Watch Video
Recommended / Complementary Product
COVALENT BONDED GLUTAMINE BIBLIOGRAPHY
1. Shabert & Ehrlich (editors;1994), Avery Publishing Group, NY. “The Ultimate Nutrient Glutamine: The Essential Non-essential Amino Acid”.
2.Grimble (1994), Annual Review of Nutrition 14, 419 – 447. “The Significance of Peptides In Clinical Nutrition”.
3. Scheppach et al. (1994), Gastroenterology 107, 429 – 434. “Effect of Free Glutamine and Alanyl-Glutamine Dipeptide on Mucosal Proliferation of the Human Ileum and Colon”.
4. Miname et al. (1992), Gastroenterology 103, 3 – 11. “Characteristics and Mechanism of Glutamine Dipeptide Absorption in Human Intestine”.
5. Adibi (1987), Metabolism 36, 1001 – 1011. “Experimental Basis For Use of Peptides As Substrates For Parenteral Nutrition”. In a Catabolic Rat Model”.
6. Adibi (1971), Journal of Clinical Investigation 50, 2266 – 2275. “Intestinal Transport of Dipeptides In Man: Relative Importance of Hydrolysis and Intact Absorption”. In a Catabolic Rat Model”.
7. Adibi & Mercer (1973), Journal of Clinical Investigation 52, 1586 – 1594. “Protein Digestion In Human Intestine As Reflected In Human Mucosal and Plasma Amino Acid Concentrations After Meals”. In a Catabolic Rat Model”.
8. Rooyackers et al. (1994), Thesis University of Limburg, The Netherlands. “Muscle Wasting and the Role of Glutamine: Metabolic Studies In a Catabolic Rat Model”.
9. Kee et al. (1994) Metabolism 43, 1373 – 1378. “The Effect of Dipeptide Structure On Dipeptide and Amino Acid Clearance In Rats”.
Product Ingredients
| Ingredients | AMT | %DV |
|---|---|---|
| Glutamine (Covalent bonded) | 5 Grams | - |
Why Buy From Us?As a trusted family- and employee-owned company for over 25 years, we've shipped more than 1 million packages, empowering our customers with expert knowledge, guiding their wellness journeys, while delivering unparalleled customer service.

Welcome to Pure Prescriptions
I founded Pure Prescriptions after overcoming Cancer at age 29, a battle that taught me the power of natural supplements and inspired me to make professional-grade, doctor-only brands accessible online—pioneering the industry over 25 years ago.
Today, still a family- and employee-owned company, we've shipped over 1 million packages, empowering countless wellness journeys with science-backed, U.S.-manufactured vitamins and supplements meticulously curated for superior quality and optimal results. Our real health experts provide personalized recommendations without upsells or gimmicks—just genuine support tailored to your needs.
Not a customer yet? We'd be thrilled to earn your trust and guide you toward vibrant health.
Sincerely,
Helpful Links:
Contact Us | LIVE Chat | Vitamin Quiz
The Pure Prescriptions Difference
When you choose Pure Prescriptions, you become part of our caring community. We’re committed to enhancing your wellness with personalized service, expertly selected products, and a dedication to your health & happiness.


Related products
Get Notified When Back In Stock
Verify you are Human:
Recently Viewed Products
-
- Vitamin Quiz
- Deals
- Shop
- Brands
- Shop by Manufacturer Brand
- Shop by Manufacturer Brand
- About
- Login