Zinc Lozenges
Zinc Lozenges – Immune Health & Antioxidant Support
Zinc Lozenges by Douglas Laboratories offer a bioavailable and convenient form of zinc to help maintain healthy immune system function and antioxidant defense. Each naturally flavored lozenge delivers 10 mg of elemental zinc as zinc citrate—an easily absorbed and gentle-on-the-stomach form of this essential trace mineral.
Comprehensive Nutritional Support:
- ✅ Supports healthy immune system activity and cellular defense
- ✅ Provides antioxidant support via superoxide dismutase (SOD) cofactor role
- ✅ May help maintain healthy skin, growth, and reproductive health
- ✅ Ideal for daily use or during times of increased immune demand
Zinc is involved in numerous biological processes and is vital for immune cell function, enzyme activity, and oxidative stress protection. This formula uses zinc citrate for excellent absorption without gastrointestinal discomfort, making it a smart choice for consistent immune health support.
Because the body cannot store large amounts of zinc, consistent dietary intake is key to maintaining optimal levels. Zinc Lozenges offer a simple, effective way to help bridge nutritional gaps—especially when dietary zinc is low or immune demands are higher.
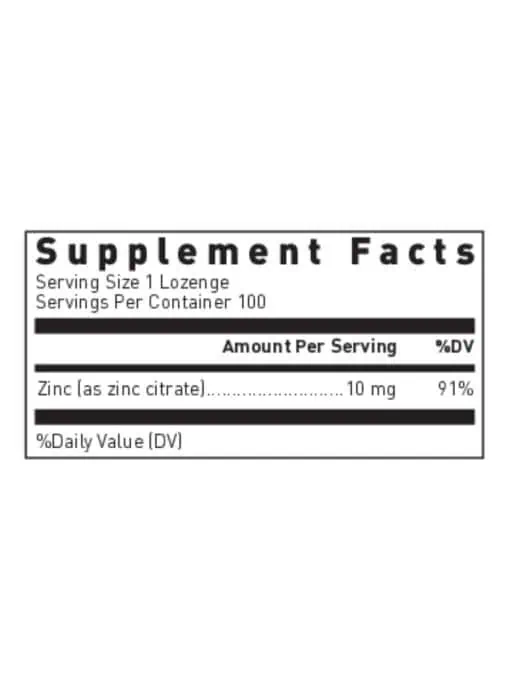
Product Ingredients
| INGREDIENTS | AMT | %DV |
|---|---|---|
| Zinc (as zinc citrate) | 10 mg | 91% |
Why Buy From Us?As a trusted family- and employee-owned company for over 25 years, we've shipped more than 1 million packages, empowering our customers with expert knowledge, guiding their wellness journeys, while delivering unparalleled customer service.

Welcome to Pure Prescriptions
I founded Pure Prescriptions after overcoming Cancer at age 29, a battle that taught me the power of natural supplements and inspired me to make professional-grade, doctor-only brands accessible online—pioneering the industry over 25 years ago.
Today, still a family- and employee-owned company, we've shipped over 1 million packages, empowering countless wellness journeys with science-backed, U.S.-manufactured vitamins and supplements meticulously curated for superior quality and optimal results. Our real health experts provide personalized recommendations without upsells or gimmicks—just genuine support tailored to your needs.
Not a customer yet? We'd be thrilled to earn your trust and guide you toward vibrant health.
Sincerely,
Helpful Links:
Contact Us | LIVE Chat | Vitamin Quiz
The Pure Prescriptions Difference
When you choose Pure Prescriptions, you become part of our caring community. We’re committed to enhancing your wellness with personalized service, expertly selected products, and a dedication to your health & happiness.


Related products
Get Notified When Back In Stock
Verify you are Human:
-
- Vitamin Quiz
- Deals
- Shop
- Brands
- Shop by Manufacturer Brand
- Shop by Manufacturer Brand
- About
- Login