Vitamin D, also fondly referred to the sunshine vitamin, is getting lots of attention these days and rightfully so, it’s an amazing nutrient! Some of the most important roles this vitamin performs for us are how we metabolize and absorb Calcium. Primarily, Vitamin D works with the Para-Thyroid Gland, utilizing how we use Calcium and other minerals to form bone. Vitamin D has also shown through several studies, to play a vital role in our immune functioning, especially when taken with other fat-soluble vitamins such as A, K and E. Studies also show that adequate Vitamin D levels help support our cardiovascular systems by supporting healthy blood pressure. Some new research indicates it also plays a key role in brain health, combatting cognitive decline acting as an antioxidant for the brain tissue, preventing oxidative damage.
Our bodies are amazing machines and we’re able to make vitamin D through sun exposure. However, it’s estimated that about 42% of the U.S. population is vitamin D deficient with some populations having even higher levels of deficiency, including premenopausal women, those with poor nutrition habits, people over age 65, Caucasians who avoid even minimal sun exposure, and those who take prescription medication long term for heartburn, acid reflux, and constipation. Studies show people with darker skin, such as African Americans and Latinos, are also at risk for lower vitamin D levels because high amounts of melanin in skin reduce the body’s ability to produce vitamin D from sunlight. In addition, certain chronic conditions—such as celiac disease, bariatric surgery, obesity, and chronic kidney or liver disease—can contribute to deficiency. And, let’s not forget those that might be getting plenty of sun exposure but use sunscreen…Sunscreen blocks the synthesis of vitamin D from UVB rays, leading to potential deficiency.
Your Skin + Sunlight = Vitamin D Production
The skin is just where this transformation begins, here; the body makes 7-dehydrocholesterol, a type of cholesterol. Carried by the bloodstream, to our liver and kidneys which then plays the vital role in the production of the finished product; 25-hydroxycholecalciferol. We then store hormone in our skin, brain, liver and fat cells.
Testing Vitamin D Levels
When you test your blood for Vitamin D, 3 types are looked at: Vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol) which comes from plant sources, Vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) is found in animal tissues, and total D, 25-Oh.
Getting our blood tested for adequate Vitamin D is important, so understand how our bodies produce and convert either sunlight or supplementation into the usable, final state. This simple blood draw can be found here.
Testing your Vitamin D level provides valuable feedback so and your physician can better understand what amounts are needed for supplementation. Toxicity is rare, but can occur, so it’s important to be tested, at least twice a year to be safe.
The Food and Nutrition Board at the Institute of Medicine provide the following guidelines when reviewing blood serum test results:
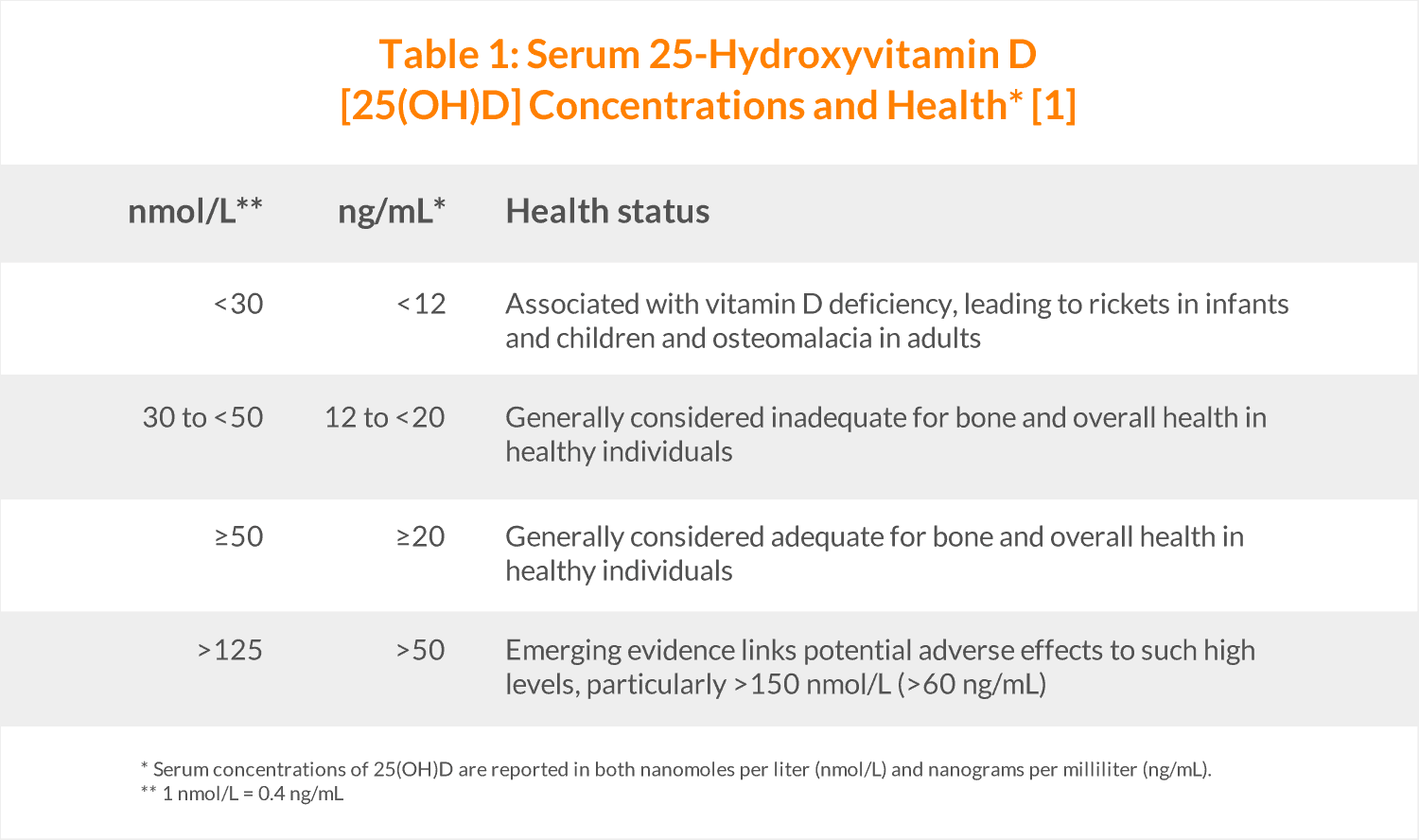
The Food and Nutrition Board (FNB) has set reference values for Vitamin D, establishing a recommended daily allowance (RDA). For those 18 and older, 4,000 IU or 15 mcg daily is considered tolerable for both men and women. The FNB has states that toxicity issues are extremely rare if taking 10,000 IU or below daily. The amount one needs daily is directly related to several factors, including skeletal and muscle health, existing chronic diseases, and para-thyroid hormone functioning.
Looking For a High Potency Vitamin D Supplement?
A great option for supplementation is our new improved Ultimate Vitamin D3 with coconut oil, available in 5000IU (125mcg) of cholecalciferol, derived from lanolin (sheep’s wool).
Potential Symptoms of Low Vitamin D
Although having a low level of vitamin D is often asymptomatic, you might experience:
- More frequent infections
- Fatigue
- Muscle or bone discomfort
- Depressed mood
If you have any of the following symptoms that are, or can be, associated with a vitamin D deficiency, then you should consult with your health-care practitioner:
- Muscle spasms and twitching (which can be anywhere but are more common in the face and around the mouth or eyes)
- Generalized weakness
- Loss of balance/falling
- Severe bone and joint pain – hip pain is most common
- Unexplained fracture
- An onset of seizures
- Abnormal heart rate or rhythm
- High blood pressure
In Conclusion
Sunny days spent outside and healthy foods may not be enough for all of us, it’s always best to know what we need through proper testing. If you feel you’re ready to supplement with Vitamin D3, we recommend getting a baseline test done to understand your personal needs and how to supplement based upon the results.
Related Product

References:
Institute of Medicine, Food and Nutrition Board. Dietary Reference Intakes for Calcium and Vitamin D. Washington, DC: National Academy Press, 2010.
https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/VitaminD-HealthProfessional/#en1
Staying Healthy with Nutrition: Elson M. Haas MD




